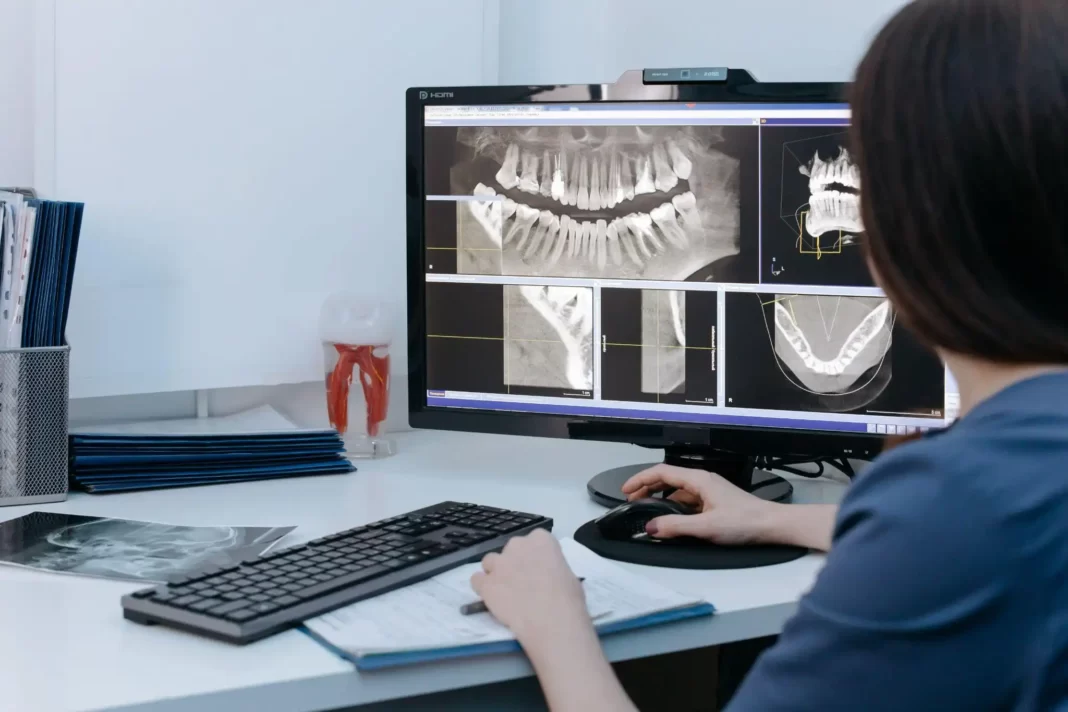
Advancements in dental imaging technology have revolutionized the field of dentistry, providing more precise and detailed information for diagnosis and treatment planning. One such advancement is the use of 3D dental X-ray, which offers enhanced visualization and comprehensive analysis of oral structures.
This article explores the evolution of dental imaging technology, with a focus on Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) and its applications in dentistry. By embracing 3D imaging, the future of dental care holds great promise for improved accuracy and precision in diagnosing and treating oral conditions.
The Evolution of Dental Imaging Technology
The evolution of dental imaging technology has significantly improved the precision and accuracy of dental X-rays. Over the years, there have been several evolutionary milestones that have contributed to this advancement.
One such milestone was the development of digital radiography, which replaced traditional film-based systems and allowed for instant image acquisition and manipulation. This revolutionary advancement not only eliminated the need for chemical processing but also reduced radiation exposure for patients.
Another significant milestone was the introduction of cone beam computed tomography (CBCT), which provided three-dimensional imaging capabilities with minimal distortion. CBCT revolutionized diagnostic capabilities by allowing for more accurate assessment of anatomical structures and improved treatment planning in areas such as implantology and orthodontics.
These evolutionary milestones in dental imaging technology have paved the way for enhanced precision and efficiency in dental care.
Understanding Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a technique used in dental imaging that allows for three-dimensional visualization of the oral and maxillofacial regions. CBCT provides high-resolution images with reduced radiation exposure compared to traditional computed tomography scans. However, it is important to consider certain limitations when using CBCT.
One limitation is its inability to capture soft tissues accurately, as the technique primarily focuses on bony structures. Additionally, artifacts can occur due to patient movement or metallic objects within the field of view. It is crucial for dental practitioners to be aware of these limitations and use CBCT judiciously.
The integration of CBCT in dental practices has revolutionized treatment planning and diagnosis. The three-dimensional images obtained through CBCT allow for a more accurate assessment of anatomical structures, aiding in implant placement, orthodontic planning, and endodontic procedures. Furthermore, CBCT assists in identifying pathologies such as impacted teeth, bone abnormalities, and tumors that may not be visible on conventional 2D radiographs alone.
The utilization of CBCT has thus significantly enhanced the precision and efficacy of dental treatments while minimizing patient discomfort and radiation exposure.
Enhancing Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
Enhancing diagnosis and treatment planning is facilitated by the integration of CBCT technology in dental practices. CBCT provides dentists with a three-dimensional view of the patient’s oral structures, allowing for improved accuracy in diagnosis and treatment planning.
By utilizing CBCT scans, dentists can assess bone density, identify pathologies such as cysts or tumors, evaluate root canal anatomy, and plan implant placement with precision. This advanced imaging technique optimizes outcomes by providing detailed information that may not be visible on conventional dental X-rays or clinical examinations alone.
With CBCT, dentists can visualize anatomical structures from multiple angles and make informed decisions regarding treatment options. Additionally, the ability to accurately measure distances and volumes aids in precise surgical planning and reduces the risk of complications during procedures.
Overall, integrating CBCT technology into dental practices enhances diagnostic capabilities and improves treatment outcomes by providing clinicians with comprehensive information for optimal decision-making.
Applications of 3D Dental X-ray in Dentistry
Applications of 3D dental imaging technology in dentistry have revolutionized the field by providing comprehensive visualization of oral structures for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
The applications of this technology are wide-ranging, offering numerous benefits to both clinicians and patients. One major application is in implant dentistry, where 3D imaging allows for precise assessment of bone quality and quantity, aiding in the selection and placement of dental implants.
Additionally, 3D dental x-rays are valuable in orthodontics, allowing for more accurate assessment of tooth positions and relationships, and facilitating better treatment planning for orthodontic interventions.
Moreover, this technology has found applications in endodontics, enabling detailed visualization of root canal anatomy and aiding in successful root canal treatments. Overall, the use of 3D dental X-rays has greatly enhanced diagnosis and treatment planning across various fields within dentistry.
The Future of Dental Care: Embracing 3D Imaging
The future of dental care involves the widespread adoption and integration of advanced 3D imaging technology, which has the potential to revolutionize diagnostics and treatment planning in dentistry.
Dental technology advancements, particularly in 3D imaging, have greatly impacted patient care by providing clinicians with a more comprehensive view of dental structures and conditions. With this technology, dentists can accurately assess the position and relationship of teeth, identify anatomical abnormalities or pathologies, and plan interventions with greater precision.
The use of 3D imaging also enables more accurate implant placement and orthodontic treatment planning. Moreover, it reduces radiation exposure for patients compared to traditional x-rays. As this technology continues to evolve, it is expected that its integration into routine dental practice will become standard, further enhancing the quality and effectiveness of dental care.